Table of Contents
Network-booting Windows PE
Windows PE (WinPE) is the Windows Preinstallation Environment, used for installation and repair of Windows computers.
Using iPXE and wimboot, you can boot into Windows PE via HTTP. You can then connect to a standard Windows file server to install a full version of Windows to the local hard disk (or to an iSCSI target).
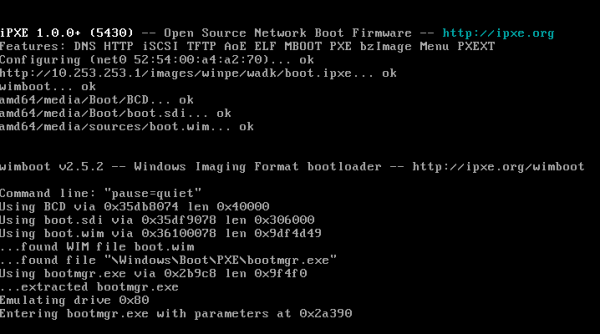
Booting Windows PE via HTTP is much faster than using traditional TFTP-based methods such as Windows Deployment Services (WDS). On a Gigabit Ethernet network, it should take less than two seconds to download a typical 200MB Windows PE image.
Setting up Windows PE
Windows PE is available as part of the Windows Assessment and Deployment Toolkit (ADK) for current versions of Windows, or as part of the Windows Automated Installation Kit (AIK) for earlier versions of Windows.
Windows Assessment and Deployment Toolkit (ADK)
The Windows Assessment and Deployment Toolkit (ADK) is compatible with Windows Server 2012, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Server 2008, and Vista.
Download and install the ADK onto a working Windows system (the “technician computer”).
From the Start menu, choose All Programs → Windows Kits → Windows ADK → Deployment and Imaging Tools Environment. This should open a command prompt window. Create 32-bit and 64-bit versions of Windows PE:
mkdir C:\temp\winpe copype x86 C:\temp\winpe\x86 copype amd64 C:\temp\winpe\amd64
Copy the contents of C:\temp\winpe to a directory on your web server (e.g. /var/www/winpe for Apache, or C:\inetpub\wwwroot\winpe for IIS).
Download the latest version of wimboot and save it to the same directory on your web server.
Create a text file boot.ipxe in the same directory on your web server, containing:
#!ipxe
cpuid --ext 29 && set arch amd64 || set arch x86
kernel wimboot
initrd ${arch}/media/sources/boot.wim boot.wim
boot
Windows Automated Installation Kit (AIK)
The Windows Automated Installation Kit (AIK) is compatible with Windows 7, Windows Server 2008, Vista, and Windows Server 2003.
Download and install the AIK onto a working Windows system (the “technician computer”).
From the Start menu, choose All Programs → Microsoft Windows AIK → Deployment Tools Command Prompt. This should open a command prompt window. Create 32-bit and 64-bit versions of Windows PE:
mkdir C:\temp\winpe copype x86 C:\temp\winpe\x86 copype amd64 C:\temp\winpe\amd64
Copy the contents of C:\temp\winpe to a directory on your web server (e.g. /var/www/winpe for Apache, or C:\inetpub\wwwroot\winpe for IIS).
Download the latest version of wimboot and save it to the same directory on your web server.
Create a text file boot.ipxe in the same directory on your web server, containing:
#!ipxe
cpuid --ext 29 && set arch amd64 || set arch x86
kernel wimboot
initrd ${arch}/ISO/boot/bcd BCD
initrd ${arch}/ISO/boot/boot.sdi boot.sdi
initrd -n boot.wim ${arch}/winpe.wim boot.wim
boot
Booting Windows PE
Boot using iPXE from the URI of your boot.ipxe script, e.g. http://my.web.server/winpe/boot.ipxe. You should see iPXE download and boot Windows PE via HTTP:
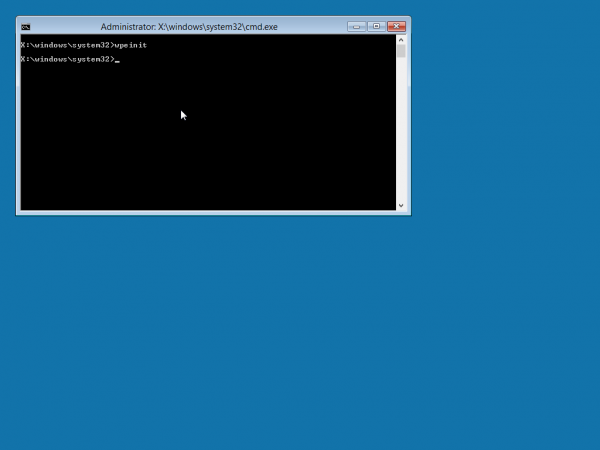
Installing Windows
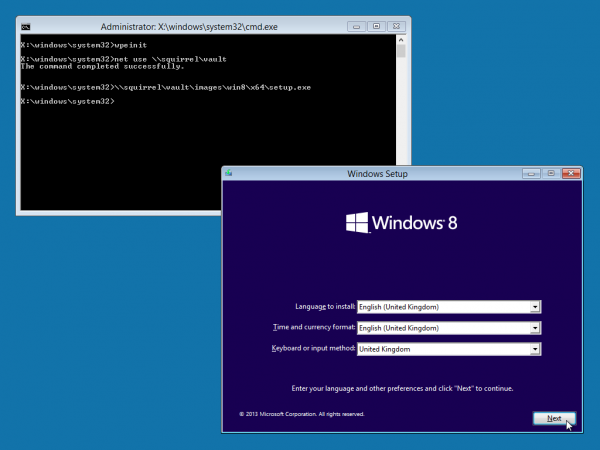
You can now connect to a Windows (or Samba) file server to run the Windows installer. For example, if you have copied the contents of your Windows installation DVD-ROM to \\myserver\installers\win8, then you can start the installer using:
net use \\myserver\installers \\myserver\installers\win8\setup.exe
Advanced topics
Adding a startup batch file
You can customise your Windows PE image so that it automatically connects to a file server and runs the Windows installer.
Create a text file install.bat containing the commands needed to connect to your file server and start the installer:
wpeinit net use \\myserver\installers \\myserver\installers\win8\setup.exe
Create a text file winpeshl.ini instructing Windows PE to run your install.bat file:
[LaunchApps] "install.bat"
Copy install.bat and winpeshl.ini to your web server and edit your boot.ipxe script to load these files:
#!ipxe
cpuid --ext 29 && set arch amd64 || set arch x86
kernel wimboot
initrd install.bat install.bat
initrd winpeshl.ini winpeshl.ini
initrd ${arch}/media/Boot/BCD BCD
initrd ${arch}/media/Boot/boot.sdi boot.sdi
initrd ${arch}/media/sources/boot.wim boot.wim
boot
When you boot into Windows PE, it should now automatically connect to your file server and run the Windows installer.
Adding a network card driver
You can customise your Windows PE image to include drivers for your network card, if your card is not already supported by Windows PE. You will need the ImageX and DISM tools, which are part of the Windows ADK (or AIK). A Linux version of imagex is also available as part of the wimlib package.
Download the drivers for your network card, and extract the driver to C:\temp\winpe\drivers. If you are using the ADK then you will need to download a driver compatible with Windows 8; if you are using the AIK then you will need a driver compatible with Windows 7.
Use ImageX and DISM to add this driver to your Windows PE image:
imagex /mountrw C:\temp\winpe\amd64\media\sources\boot.wim 1 C:\temp\winpe\amd64\mount dism /image:C:\temp\winpe\amd64\mount /add-driver /driver:c:\temp\winpe\drivers /recurse imagex /unmount /commit C:\temp\winpe\amd64\mount
Installing to an iSCSI target
You can use your Windows PE image to install Windows to an iSCSI target. Create a text file install.ipxe containing:
#!ipxe prompt -k 0x197e -t 2000 Press F12 to install Windows... || exit chain boot.ipxe
and copy it to the directory on your web server containing your boot.ipxe script.
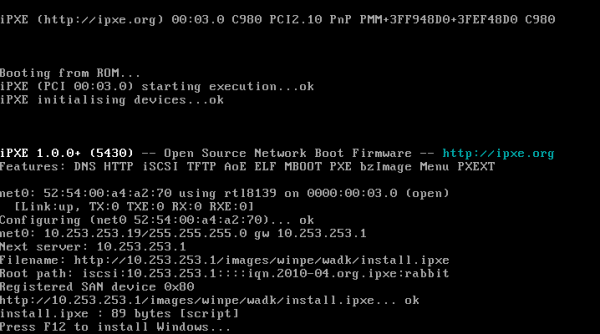
Configure your DHCP server to provide the URI of your install.ipxe script as the boot filename, and the SAN URI of your iSCSI target as the root-path. If your iSCSI target uses access control lists (ACLs), then you may also need to provide the correct initiator-iqn.
You should see the diskless computer connect to the iSCSI target and then prompt you to ”Press F12 to install Windows”:
Press F12 to begin the installation process. If you have already added a startup batch file as described above, then the Windows installer will start automatically. If not, then connect to your file server and run the Windows installer manually.
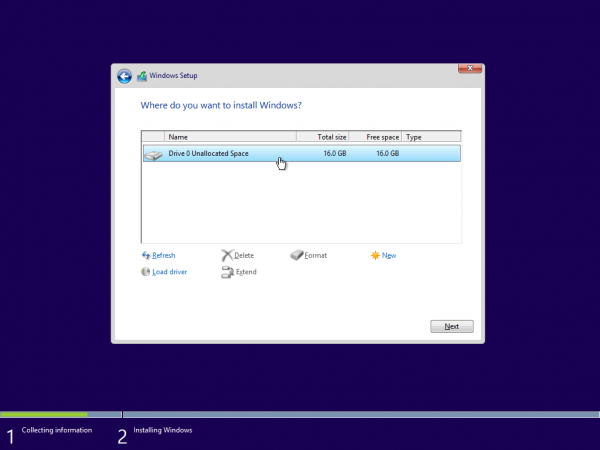
Proceed to install Windows as usual. When you reach the ”Where do you want to install Windows?” screen, you should see the iSCSI disk appear as a possible install location: